The U.S. health innovation ecosystem stands as a global beacon of progress, characterized by a unique collaboration between academia, industry, and government entities. Spanning back to its roots during World War II, this ecosystem has effectively harnessed public-private partnerships to advance biomedical research and technology. Federal funding, most notably through agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has played a crucial role in fostering groundbreaking innovations in medicine and beyond. This synergy has not only propelled advancements in healthcare but has also paved the way for a rich history of health innovation that continues to evolve today. As challenges in public health emerge, the resilience and adaptability of the U.S. health innovation landscape become ever more significant in addressing these pressing issues.
The American healthcare innovation landscape is renowned for its dynamic interplay of academic research, industry collaboration, and government support. This collaborative framework has been pivotal in driving advancements in medical science and technology throughout history. Significant investment from federal sources facilitates the development of novel therapies and enhances research capabilities across various disciplines. The evolution of this ecosystem captures the essence of how strategic alliances and innovative funding strategies can transform healthcare outcomes. By examining the foundational elements of this ecosystem, one can understand its importance in shaping the future of health solutions.
The Historical Roots of the U.S. Health Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem has its origins rooted in the collaboration between government and academia, with significant milestones dating back to World War II. During this tumultuous period, the federal government recognized the urgent necessity for technological advancements, especially in biomedical research, to support the war effort. This led to the establishment of public-private partnerships that galvanized academic institutions and private industries towards a common goal of innovation. For instance, the coordinated efforts of scientists at universities and private firms in developing antibiotics like penicillin not only saved lives during wartime but also set the foundation for future research and advancements in healthcare.
This period marked the birth of a systematic approach to health innovation in the U.S., with federal funding playing a crucial role. The initiation of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) during the war was a turning point, fostering collaborations that previously did not exist. It highlighted how a strategic alliance between federal entities and private sector expertise could lead to breakthroughs in medical technology. The engagement of thousands of scientists laid down the groundwork for what would evolve into a robust health innovation system, illustrating the historical significance of federal partnerships in the realm of biomedical research and beyond.
The Impact of Federal Funding on Biomedical Research
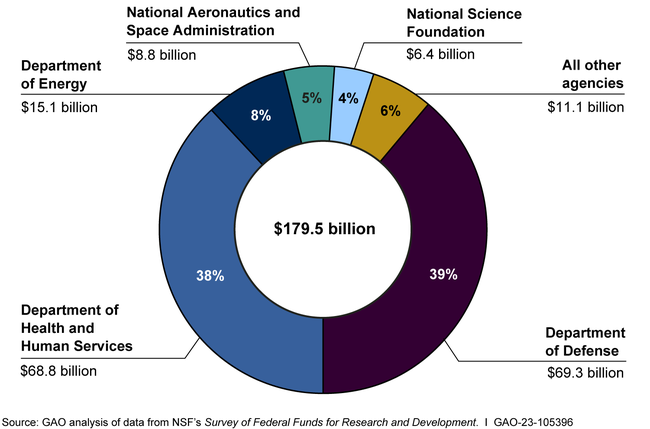
Federal funding has been a cornerstone of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem, particularly in the enhancement of biomedical research. Over the decades, organizations like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have successfully channeled government resources into training, research, and infrastructure development. This financial backing has not only propelled academic research but has also catalyzed the creation of new therapies and technologies that have transformed patient care. As federal investments have increased, they have often prompted additional private funding, creating a virtuous cycle of innovation and growth within the health sector.
However, recent challenges to federal funding models, such as proposed cuts to NIH budgets, raise concerns about the sustainability of this innovation ecosystem. Critics argue that limitations on reimbursement for indirect costs could hinder biomedical research’s trajectory, potentially stalling progress on critical health issues. The historical reliance on federal funding underscores its pivotal role in the ecosystem; thus, safeguarding that investment is crucial for maintaining U.S. leadership in global health innovation.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Model for Health Innovation
Public-private partnerships have been instrumental in advancing health innovation in the United States, acting as a bridge between academic research and practical application in the private sector. The collaboration model formed during World War II has evolved to encompass a wide array of disciplines within biomedicine, resulting in numerous breakthroughs in medical technology and drug development. These partnerships enable sharing of resources, expertise, and funding, leading to innovations that might not be possible through isolated efforts.
Today, partnerships between universities, government entities, and private industries continue to thrive, driving forward U.S. health innovation. Through collaborative research initiatives, new therapies are developed more swiftly, responding to public health needs more effectively. By leveraging the strengths of each sector—government support, academic rigor, and industry agility—public-private partnerships maintain a dynamic innovation ecosystem that not only contributes to health advancements but also serves as a global template for other nations aiming to achieve similar successes.
The Evolution of Biomedical Research in the U.S.
The evolution of biomedical research in the U.S. is a testament to the collaborative efforts among various stakeholders over the last eight decades. With its origins in wartime necessity, the field has transformed into a sophisticated domain fueled by both public and private investments. The establishment of rigorous research methodologies, regulatory frameworks, and the proliferation of funding mechanisms have collectively enhanced the capabilities of the biomedical research landscape. Universities have become research powerhouses, building infrastructures that support advanced scientific inquiries.
The growth of the sector has been characterized by significant advancements in technologies and therapies, showcasing the potent combination of government-backed initiatives and private sector innovation. This evolution doesn’t just represent progress within the field; it embodies a fundamental shift in how health innovation is approached. The cooperative spirit that underscored the initial efforts has laid the groundwork for a thriving ecosystem that remains the envy of the world today.
Challenges Facing the U.S. Health Innovation Ecosystem
Despite its achievements, the U.S. health innovation ecosystem faces several challenges that could impede future progress. Increasing scrutiny over federal funding, particularly from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has sparked debates about the sustainability of current research practices. With proposals to limit reimbursements for indirect costs, many researchers fear that crucial funding may be curtailed, directly impacting the breadth of biomedical research. This environment of uncertainty complicates the planning and execution of long-term research initiatives.
Moreover, as the pace of scientific discovery accelerates, the need for adaptation and flexibility within the ecosystem becomes paramount. Drug development timelines are lengthy and costly; thus, ensuring that funding mechanisms are adaptive and supportive of innovative research strategies is essential. The ability to navigate these challenges will determine the future trajectory of health innovation in the U.S., necessitating strong advocacy from researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders to sustain a robust and effective health innovation ecosystem.
The Role of NIH in Shaping Health Innovation
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) plays a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of health innovation in the United States. As the primary federal agency responsible for biomedical research funding, the NIH has established a framework that supports transformative research efforts across various fields of healthcare. Historically, the NIH has provided essential funding that enables scientists to pursue novel ideas and develop groundbreaking therapies. This funding not only supports individual research projects but also helps cultivate the next generation of biomedical researchers, ensuring a continuous pipeline of innovation.
Moreover, the NIH’s investment in public-private partnerships exemplifies its commitment to enhancing the translational potential of academic research. By collaborating with private industry, the NIH facilitates the movement of research from the lab to the marketplace, driving the development of new medical interventions. This unique position enables the NIH to bridge gaps within the health innovation ecosystem, fostering collaborations that can amplify the impact of research funding and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
Historical Lessons from War: Innovations in Urgent Times
The historical lessons learned from wartime efforts highlight the importance of rapid innovation in urgent circumstances. During World War II, the U.S. faced significant health challenges that necessitated immediate action, particularly concerning soldiers’ health and performance. The creation of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was a response to this need, bringing together government, academia, and industry to address pressing health issues head-on. The successful development and mass production of penicillin exemplified how organized research efforts could lead to monumental breakthroughs even in the face of constrained timelines.
The collaborative strategies employed during this critical period continue to inform modern approaches to biomedical research. Current health crises, such as pandemics or public health emergencies, require similarly swift and coordinated responses. Leveraging historical partnerships and funding frameworks can provide valuable insights for responding effectively to contemporary challenges, reinforcing the significance of a resilient health innovation ecosystem capable of adapting to new pressing demands.
Future Directions for American Health Innovation
Looking ahead, the future of American health innovation hinges on our capacity to evolve and adapt in response to emerging challenges and opportunities. As novel technologies like artificial intelligence and genomics gain traction, the health innovation ecosystem must embrace these advancements to sustain its competitive edge. This involves not only increasing research funding but also ensuring that regulatory frameworks are conducive to innovative practices. The ongoing development of precision medicine and personalized therapies holds immense potential for transforming patient care and requires a collaborative approach among various stakeholders.
In addition to advancing technologies, fostering diversity and inclusion within the health innovation ecosystem is critical for future success. Engaging a wider range of voices and perspectives can lead to more innovative solutions and broaden participation in biomedical research. Policymakers, industry leaders, and academic institutions should prioritize inclusivity and equity in health innovation to ensure that the benefits of scientific advancements reach all segments of the population. By combining cutting-edge technology with a commitment to diversity, the U.S. can continue to lead the world in health innovation for decades to come.
Global Impact of the U.S. Health Innovation Ecosystem
The global impact of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem cannot be overstated; it serves as a model for countries worldwide, demonstrating how effective collaboration between government, academia, and the private sector can yield significant advancements in healthcare. This ecosystem has led to numerous breakthrough therapies and technologies that have improved health outcomes globally. The research conducted in the U.S. often feeds into international initiatives, establishing a worldwide standard for biomedical research practices and prompting other nations to adopt similar collaborative frameworks for health innovation.
Furthermore, the U.S. health innovation system has positioned itself as a pivotal leader in addressing global health challenges, including infectious diseases, chronic conditions, and health crises. The ability to mobilize resources efficiently and respond to emerging health threats swiftly has solidified the U.S.’s role in global health arenas. By sharing knowledge, therapies, and technologies with other nations, the U.S. not only enhances its own health innovation landscape but also plays a crucial part in fostering a healthier world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of public-private partnerships in the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
Public-private partnerships are crucial in the U.S. health innovation ecosystem as they leverage the strengths of both sectors to drive advancements in biomedical research. These collaborations enable the sharing of resources, expertise, and funding, which fosters innovation and accelerates the development of new technologies and treatments.
How has NIH innovation contributed to the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
NIH innovation is at the heart of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem, providing substantial federal funding for biomedical research. By supporting promising projects and enabling researchers to explore novel ideas, the NIH helps transform academic discoveries into practical applications, significantly enhancing public health outcomes.
What historical events shaped the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem took shape during World War II, when federal funding and collaboration between government, industry, and academia were established to address urgent medical challenges. This proactive approach laid the groundwork for today’s system, characterized by strong public-private partnerships and a continued focus on biomedical research.
Why is federal funding important for the U.S. health innovation ecosystem?
Federal funding is vital for the U.S. health innovation ecosystem as it provides the necessary resources for basic and applied biomedical research. This funding facilitates collaborations that lead to breakthroughs in medical technology, ensuring that innovation remains robust and responsive to health challenges.
How does the history of health innovation influence current biomedical research in the U.S.?
The history of health innovation in the U.S. showcases the evolution of collaboration between government, academia, and industry, particularly since World War II. This legacy continues to influence current biomedical research by encouraging adaptive strategies and funding models that nurture innovation and lead to impactful health solutions.
What challenges does the U.S. health innovation ecosystem currently face?
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem faces challenges such as potential cuts to federal funding, evolving regulatory landscapes, and the need to maintain robust public-private partnerships. Navigating these challenges is crucial to sustaining the momentum of biomedical innovation and ensuring equitable access to advancements in healthcare.
How do public-private partnerships enhance biomedical research outcomes in the U.S.?
Public-private partnerships enhance biomedical research outcomes by integrating academic knowledge with industry expertise. This collaboration accelerates the translation of research findings into practical applications, leading to more timely and effective medical solutions that benefit public health.
What impact does federal funding have on the future of U.S. biomedical research?
Federal funding is essential for the future of U.S. biomedical research as it drives innovation initiatives, supports young researchers, and sustains the long-term projects necessary for groundbreaking discoveries. A stable funding environment will ensure that the U.S. remains a leader in health innovation globally.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. health innovation ecosystem became strong post-World War II, thanks to government-funded research that led to breakthroughs like penicillin. |
| Partnerships between the federal government and academia fostered significant advancements in biomedicine and technology. |
| Research funding from federal sources has been pivotal in supporting scientific education and public-private collaboration. |
| The establishment of organizations like the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) helped coordinate wartime scientific efforts leading to long-term benefits. |
| Challenges exist today regarding federal funding cuts, which threaten the basis of successful research partnerships. |
Summary
The U.S. health innovation ecosystem is an unparalleled model of success that showcases the power of public-private partnerships in driving medical advancements. With roots tracing back to World War II, these collaborations laid the groundwork for a thriving biomedical industry that continues to innovate and respond to health challenges today. Amid current scrutiny of federal funding, it remains crucial to preserve the systems that have allowed for significant breakthroughs in healthcare and research. Maintaining the strength of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem is essential for addressing future health crises and ensuring sustained economic growth.