Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked a lively debate among nutritionists and health experts. While sugar is not categorized as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, its consumption can lead to genuine sugar cravings that mimic addictive behaviors. Many people find themselves reaching for sugary snacks and beverages, often leading to a cycle of compulsive eating that has noticeable health effects. In fact, attempting to reduce sugar intake can result in unpleasant sugar withdrawal symptoms, illustrating how deeply ingrained sugar is in our diets.
Exploring the nature of sugar consumption reveals intriguing insights about our habits and cravings. While sugar is often discussed alongside other substances known for causing dependency, such as caffeine or recreational drugs, its role in our everyday diets is inherently different. The pervasive presence of sweetened foods can lead to habitual patterns that are challenging to break, despite their necessity for maintaining a balanced diet. As we examine the implications of reducing added sugars, it’s essential to consider how these sugary delights can shape our health and behavior, influencing everything from energy levels to psychological wellbeing.
Understanding Sugar Addiction: Is Sugar Addictive?
The question of whether sugar is addictive remains a heated topic among nutritionists and researchers. While substances like alcohol and nicotine have defined clinical addiction criteria, sugar is often viewed through a different lens. It has been shown that sugar can trigger cravings and drive compulsive eating behaviors much like addictive substances. However, because it doesn’t fit precisely into the definition of addiction as outlined in clinical guidelines, it’s essential to approach the discussion of sugar’s addictive qualities with nuance. Just because sugar may lead to cravings does not automatically classify it as an addictive substance in the same category as more harmful drugs.
The nuances of sugar consumption become even more complex when examining the health effects of sugar on the body. Sugar is prevalent in many foods we consume, including fruits and dairy, implying our bodies are not only wired to accept it but also require it in moderate amounts. The health effects kick in primarily when we consume added sugars in high quantities, which can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when cut out abruptly. Understanding that one’s cravings for sugar can stem from its omnipresence in ultra-processed foods sheds light on why people might struggle with reducing their sugar intake.
Sugar Cravings: The Science Behind Them
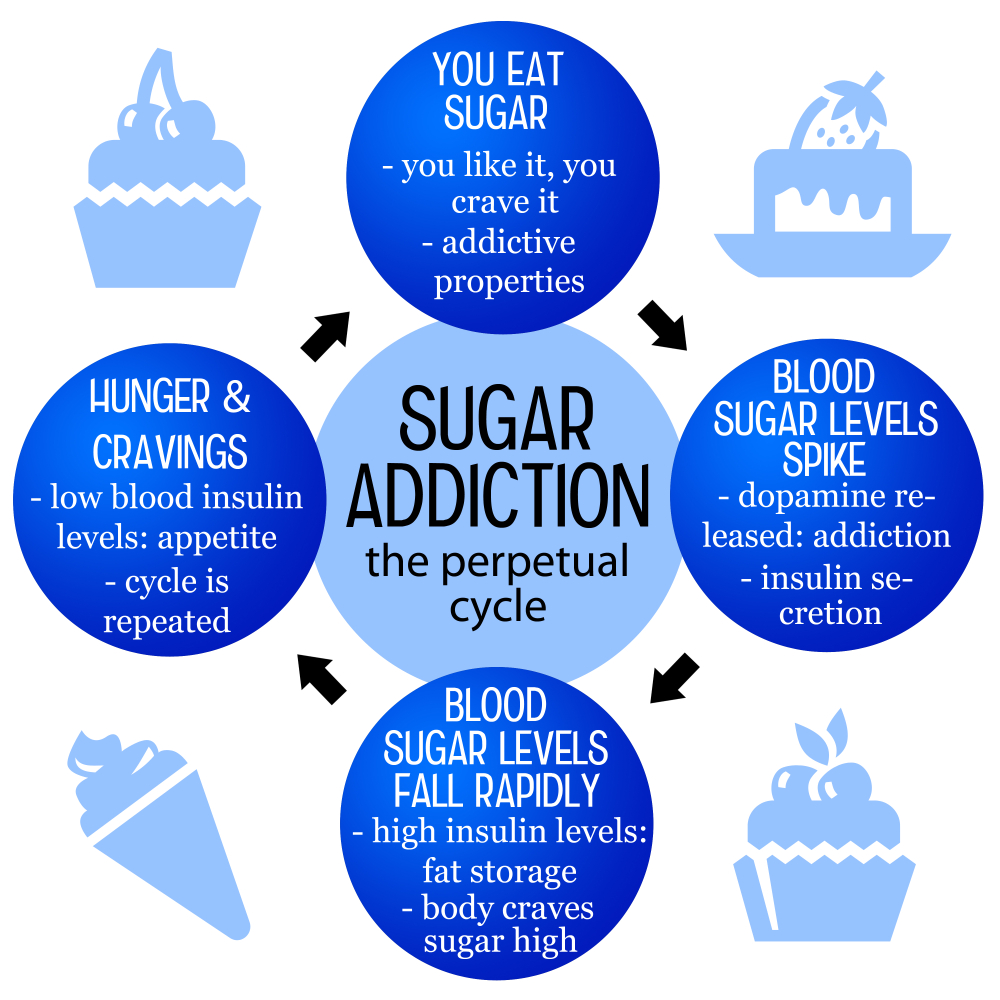
Cravings for sugar can feel overwhelming, and the science behind these intense desires is deeply rooted in both psychology and biology. When we consume sugar, our brains release dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a significant role in pleasure and reward. This reaction can lead to a cycle of seeking out sugary foods as a source of comfort or reward. Knowing the underlying mechanism behind sugar cravings can help individuals better understand their eating habits and the reasons behind their compulsion to reach for sweets, which can feel akin to other addictions.
Additionally, the presence of sugar in many mass-produced food items has increased the likelihood of developing cravings over time. When consuming ultra-processed foods overloaded with sugar, the body begins to rely on these highs to function normally. Reducing sugar intake can cause temporary withdrawal symptoms, as the brain must recalibrate to lower levels of dopamine. Understanding this cycle is crucial for those aiming to break their dependence on sugary foods, inviting them to explore healthier substitutes and strategies for managing their cravings.
Health Effects of Sugar: Beyond the Cravings
The health effects of sugar intake have become a critical area of concern for many nutritionists and public health professionals. High levels of added sugar have been linked to numerous negative health outcomes, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. In recent years, there has been a growing acknowledgement of the need to monitor and reduce sugar consumption in our diets. The average American’s consumption of added sugars far exceeds recommended limits, thereby increasing health risks and raising alarming concerns about our modern dietary habits.
Moreover, it’s essential to recognize that the body doesn’t always handle sugar in isolation; sugar’s effects are exacerbated by the types of foods consumed alongside it. Diets high in sugar and unhealthy fats can lead to metabolic complications, which can further interfere with our health. Hence, understanding the health effects of sugar not only emphasizes the need for moderation but also encourages a more balanced approach to nutrition, advocating for whole foods and naturally occurring sugars to replace highly processed options.
Reducing Sugar Intake: Practical Tips for Success
Reducing sugar intake is paramount for improving overall health, yet the process can be challenging. One practical approach is to gradually cut back on added sugars rather than attempting complete elimination all at once. This method can help mitigate withdrawal-like symptoms, making the transition smoother and more sustainable. Reading food labels and getting familiar with the different names of sugar can empower individuals to make informed choices while grocery shopping, reducing hidden sources of added sugars in their diets.
Another effective strategy for reducing sugar intake involves incorporating more whole, unprocessed foods into daily meals. Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can naturally curb sugar cravings by providing sustained energy and satiety. In tandem with regular physical activity, these dietary changes can lead to long-term improvements in health and well-being and may diminish dependence on sugar-heavy snacks. By making these gradual lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve better health outcomes while still enjoying the occasional treat.
Navigating Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms: What to Expect
When reducing sugar intake, many individuals encounter withdrawal symptoms that can be unexpected and uncomfortable. Symptoms may include headaches, irritability, mood swings, and cravings, mirroring those that individuals experience when attempting to quit addictive substances. It is vital to recognize these symptoms as part of the body’s adjustment process rather than a sign of failure. They often diminish in intensity over time as the body adapts to lower sugar levels, allowing individuals to regain control over their eating habits and cravings.
Anticipating sugar withdrawal symptoms can prepare individuals for a smoother transition when cutting back on sugar. Staying hydrated, eating nutrient-dense foods, and engaging in regular physical activity can support the body’s recovery and lessen the severity of withdrawal symptoms. Understanding that these experiences are temporary can motivate individuals to stay committed to their sugar-reduction goals, ultimately leading to a more balanced approach to eating and improved health.
Balancing Sugar Consumption with Healthy Choices
Finding a balance between enjoying sugar and maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for overall well-being. It is important to acknowledge that sugar does have a place in our diet, primarily when consumed in moderation. Rather than demonizing sugar, focusing on moderation and making intentional choices can foster a healthier relationship with food. Learning to enjoy the natural sweetness found in fruits and other whole foods allows individuals to satisfy their cravings without resorting to excessive amounts of processed sugars.
Additionally, substituting high-sugar processed foods with healthier alternatives is key to striking the right balance. Incorporating naturally sweet foods and using spices like cinnamon or vanilla can enhance flavor without the extra sugar. By creating a diverse and colorful plate that prioritizes whole foods, individuals can maintain their joy of eating while effectively managing their sugar intake. This balanced approach promotes a sustainable relationship with food, ensuring that there’s space for sweetness without compromising health.
The Link Between Sugar and Emotional Eating
Emotional eating is a behavior that many people experience when dealing with stress, sadness, or anxiety, and sugar often finds its way into this equation. The comfort derived from sugary treats can lead to a cycle where individuals seek out sugar as a source of relief from emotional discomfort. Understanding the connection between emotional states and sugar cravings can empower people to find healthier coping mechanisms. Instead of reaching for sweets, exploring mindfulness techniques or engaging in physical activity can serve as alternative outlets for managing emotions.
Moreover, developing a deeper awareness of emotional triggers can help individuals identify the situations that prompt sugar cravings. Keeping a food and mood journal can assist in this process, allowing individuals to document patterns and better understand their behaviors. By recognizing that sugar is often a temporary solution to deeper emotional issues, individuals can work towards addressing the root causes of their emotional eating and gradually create a more balanced, healthier approach to dealing with their feelings without relying solely on sugar.
The Importance of Nutrition Education on Sugar Intake
Investing in nutrition education is vital to equip individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed choices about sugar intake. Many people remain unaware of the significant health consequences associated with excessive sugar consumption. By fostering a greater understanding of the health effects of sugar, including its role in chronic diseases such as obesity and diabetes, individuals can become more motivated to regulate their sugar consumption consciously. Public health initiatives can play a critical role by promoting educational resources and campaigns that emphasize the risks of high sugar intake.
Furthermore, nutrition education should extend beyond basic knowledge to include practical strategies for reducing sugar intake. Teaching individuals how to read food labels, understand sugar content in various foods, and explore healthier alternatives empowers them to take control of their dietary choices. As people become more informed, they can navigate the complexities of modern diets and reduce their reliance on sugar-laden products, ultimately contributing to improved overall public health and well-being.
Sugar in Context: Distinguishing Between Healthy and Unhealthy Sources
Understanding the different sources of sugar in our diets is crucial in managing sugar consumption effectively. Not all sugars are created equal; naturally occurring sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy offer essential nutrients and health benefits, while added sugars in processed foods contribute to health risks without offering nutritional value. Fostering an appreciation for the role of naturally occurring sugars can help individuals enjoy sweet flavors without over-consuming unhealthy versions that dominate the modern food landscape.
This distinction is vital for those seeking to reduce sugar intake successfully. By prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can increase their intake of beneficial nutrients while minimizing added sugars. Being mindful of sugar sources helps empower healthier food choices, ensuring individuals can maintain a balanced diet without sacrificing satisfaction. Adopting this clear view of sugar in context promotes a healthier relationship with food and encourages better long-term dietary habits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like other substances such as alcohol and nicotine?
While sugar can increase cravings and may lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not clinically classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The psychological and physical effects are real, but the severity of withdrawal symptoms is not comparable to those of true addictive substances.
What contributes to sugar cravings and how can I manage them?
Sugar cravings can stem from the consumption of ultra-processed foods that are high in added sugars, fats, and sodium. To manage these cravings, it’s advisable to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than quitting cold turkey, as sudden cessation can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar intake can lead to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The average American consumes about 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, significantly above the American Heart Association’s recommendations of 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. Monitoring and managing sugar intake is vital for health.
What are the symptoms of sugar withdrawal when reducing sugar intake?
When reducing sugar intake, some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms similar to those associated with addictive substances. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, and anxiety, which can occur due to the body’s adjustment to lower sugar levels.
How can I reduce my sugar intake effectively?
To effectively reduce sugar intake, start by gradually cutting back on added sugars in your diet. Read food labels carefully to identify high-sugar products and consider substituting them with healthier options. This slow approach can mitigate cravings and allow your palate to adjust over time.
Can sugar be part of a healthy diet?
Yes, sugar can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy are essential for nutrition, while added sugars should be limited. Enjoying sweet flavors can enhance meals, but it’s crucial to balance them within dietary guidelines.
Is there a safe amount of sugar to consume daily?
According to the American Heart Association, men should limit their intake to no more than 9 teaspoons and women to 6 teaspoons of added sugar per day. Staying within these guidelines can help minimize health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption.
How do sugar withdrawal symptoms compare to those of addictive substances?
Sugar withdrawal symptoms can include mild headaches, dizziness, and anxiety but are generally less severe compared to withdrawal from substances like alcohol or nicotine, which can produce more intense physiological effects and cravings.
Do ultra-processed foods influence sugar addiction?
Yes, ultra-processed foods, which are high in added sugars, fats, and sodium, can increase cravings due to their palatability and accessibility. This habitual consumption can lead to increased sugar intake, making it harder to reduce sugar consumption without experiencing cravings.
What is the role of sugar in the diet?
Sugar plays a role in the diet by enhancing flavor and texture, contributing to pleasure in eating. While it’s important to limit added sugars, natural sugars found in wholesome foods are necessary for balanced nutrition.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Addiction Classification | Sugar is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol, nicotine, or opiates. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | While sugar can increase cravings and compulsive eating, the withdrawal symptoms are milder than those from drugs. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | These foods, loaded with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, heighten cravings and habitual consumption. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons of added sugar for men, 6 teaspoons for women. |
| Moderation Importance | Consumption of sugar in moderation can enhance flavor and is necessary in a balanced diet. |
| Gradual Reduction | Going cold turkey can lead to negative effects; it’s better to gradually reduce sugar intake. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question sparks considerable debate in nutrition science. Although sugar exhibits some addictive qualities through increased cravings, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The key lies in moderation and understanding that while we can reduce sugar intake for health benefits, it is also a necessary component of a balanced diet found in many essential foods. Awareness of our sugar consumption, particularly from ultra-processed foods, is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Overall, while sugar may create cravings, its management rather than complete avoidance is essential.