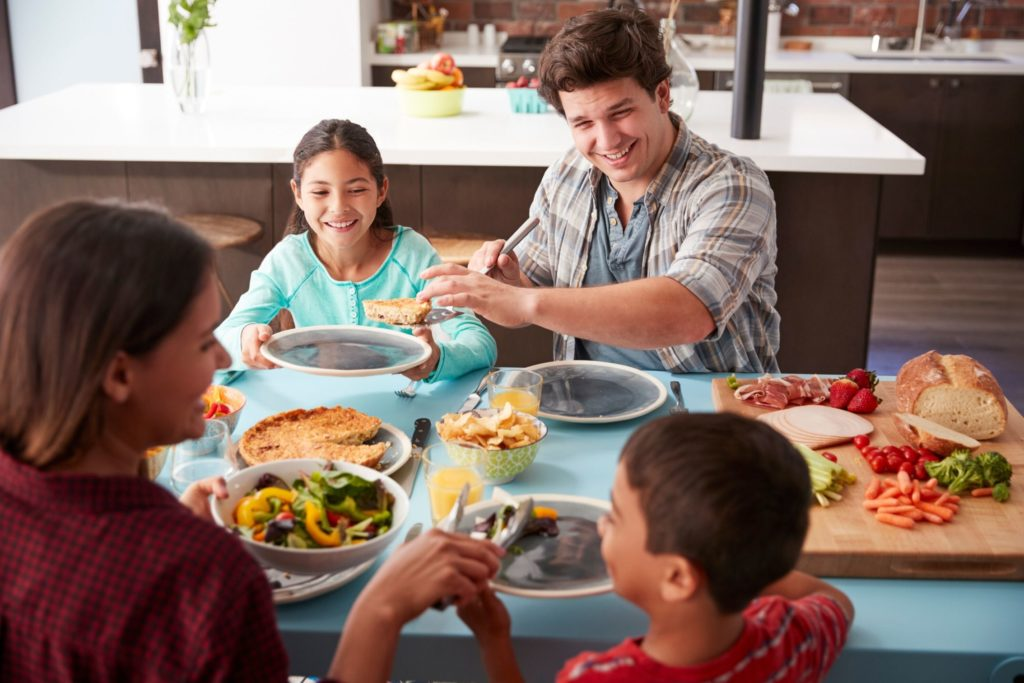
Shared meals and happiness are deeply intertwined, as recent studies reveal that the act of dining with others can significantly enhance our overall well-being. Whether it’s a casual lunch with friends or a festive family dinner, social eating fosters connections that lead to greater mealtime happiness. Data from the World Happiness Report indicates that people who regularly share meals report higher satisfaction with life and a more positive emotional state. In fact, this connection might be a more reliable indicator of contentment than traditional metrics such as income or employment status. As social isolation becomes a growing concern, understanding the role of shared meals as vital to our mental health could inspire meaningful changes in how we connect with others.
The concept of communal dining is gaining attention as a pivotal factor in enhancing individual joy and fulfillment. Engaging in meals with family, friends, or even acquaintances serves as a powerful platform for reinforcing bonds and celebrating togetherness. Happiness studies suggest that these social gatherings may contribute not only to immediate pleasure but also to long-term well-being indicators. Instead of merely focusing on economic success, we might consider how social interactions during meals can uplift spirits and enhance our collective happiness experience. As society grapples with widespread isolation, the importance of coming together over food has never been more essential.
The Link Between Social Eating and Emotional Well-Being
Social eating is increasingly recognized as a key component of emotional and psychological well-being. Studies have shown that people who share mealtimes with family and friends experience a remarkable increase in life satisfaction. These shared meals foster connections that can lead to more positive emotions, forming a harmonious environment reflective of well-being indicators. When individuals gather around a table, they engage in meaningful conversations, share experiences, and build relationships, which are crucial for emotional health.
Additionally, social eating enhances the quality of relationships, contributing effectively to overall happiness. Engaging in meals with others provides an opportunity to create joyful memories and develop deeper bonds. When families or friends come together to share food, they do not just share nutrition, but also laughter and companionship, which are essential for cultivating a fulfilled life. Furthermore, happiness studies continually affirm that these interactions can serve as both preventative measures against isolation and as catalysts for a more satisfying life.
Shared Meals and Happiness: An Effective Indicator
Recent findings highlight that shared meals might be a more reliable indicator of happiness than traditional measures such as income. According to the World Happiness Report, the frequency of shared meals correlates directly with individuals’ self-reported happiness levels. This suggests that social eating may reflect deeper elements of well-being that go beyond mere financial stability. Consequently, policymakers and social scientists are urged to consider the number of shared meals as a significant metric when assessing community quality of life.
This correlation emphasizes that happiness is multifaceted and that social connectivity, reinforced through shared dining experiences, may play a vital role in psychological health. As we witness the trend of individuals dining alone rise significantly over the past few decades, it stresses the need for initiatives aimed at promoting social eating. Encouraging people to dine together not only serves potential benefits for individual happiness but could also positively influence societal health by reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation.
The Decline of Dining Together: Implications for Society
The increasing prevalence of dining alone has raised concerns among researchers who highlight its negative implications on emotional health. As reported by the American Time Use Survey, many individuals now find themselves consuming meals in solitude, which could diminish opportunities for nurturing relationships and enjoying the emotional benefits that come from social dining. Over time, the absence of regular shared meals can contribute to an increase in social isolation and its associated mental health issues, reinforcing the pressing need to address this trend.
The implications of this decline extend beyond personal happiness; they resonate within communities, potentially leading to weakened social bonds and lack of civic engagement. Recognizing the importance of shared meals in fostering community ties suggests that initiatives promoting social eating could significantly improve communal well-being. As policymakers explore strategies to counteract loneliness and bolster mental health, incorporating dining together as a focus could be a vehicle for reviving social connections and enhancing collective resilience.
Causal Relationship: Do Shared Meals Create Happiness?
A central question in current happiness studies revolves around the causal relationship between shared meals and happiness. While the evidence indicates a strong correlation, the challenge remains to determine whether dining with others actively fosters happiness or if happier individuals are simply more inclined to share meals. This distinction is crucial in understanding how to effectively enhance emotional well-being through social eating. Micah Kaats highlights the importance of future research to dissect this dynamic more thoroughly.
For many, the practice of dining together elicits joyful feelings, suggesting a reciprocal relationship where sharing meals might lead to increased happiness. The anecdotes of people expressing gratitude after enjoying a hearty meal with loved ones reinforce the idea that these moments can create lasting positive emotional states. Ultimately, establishing this causal link could empower researchers to develop targeted interventions that encourage shared meals and, in turn, promote greater happiness across various demographics.
Social Indicators: Measuring Happiness Through Meals
Using the frequency of shared meals as a solid metric for measuring happiness offers a unique perspective in social science research. Researchers can glean insights into community well-being by analyzing dining patterns among individuals. Unlike traditional measures of happiness, which can be subjective and variable, the act of sharing meals provides more objective data, as individuals can easily recall recent shared dining experiences. Kaats advocates for utilizing this straightforward question in assessments of societal happiness and trust.
Moreover, this approach could act as a bridge linking various other social indicators to overall happiness assessments. For example, the interaction between meal sharing and local civic engagement can yield valuable data on both community health and individual satisfaction. Emphasizing meal sharing as a cornerstone of happiness could encourage individuals and communities to prioritize social interactions, reinforcing the idea that collective well-being is fundamentally grounded in our daily lives.
Creating Policies to Encourage Shared Meals
As researchers unpack the importance of shared meals in relation to happiness, there is an emerging call for policies that encourage communal dining experiences. Local community programs, initiatives in schools, and workplace environments that promote shared meals could play a transformative role in enhancing societal well-being. These efforts not only foster social connections but also contribute to a culture of inclusivity and joy that benefits everyone involved.
Moreover, creating public spaces designed for communal dining can serve as a springboard for relationships and happiness. By providing accessible venues where people can gather, governments and organizations can support the cultivation of community ties. This approach represents a proactive stance against the trend of solitary dining, positioning shared meals as an integral element of societal health and well-being.
The Quantifiable Benefits of Shared Meals
Quantifying the benefits of shared meals extends beyond emotional satisfaction; it also encompasses physical health implications. Social eating encourages mindful consumption and can lead to healthier dietary choices, as individuals are more likely to enjoy balanced meals when dining with others. This aspect underlines the significance of meal sharing not just as a social activity but as a pillar of healthy living, thoroughly linked to both physical and mental happiness.
Furthermore, meal sharing often incorporates diverse cultural practices and cuisine, enriching individuals’ gastronomic experiences while contributing to well-being. This combination of social interaction and dietary variety promotes not just happiness but also educational engagement with food practices from various cultures. Therefore, fostering an environment where shared meals are celebrated can lead to myriad benefits that encompass joy, health, and enlightenment.
Repurposing Mealtime: From Necessity to Celebration
Transforming mealtime from a mundane necessity to a cherished experience can significantly impact overall happiness. Reimagining how we approach meals—viewing them as opportunities for connection rather than mere routines—can reshape our societal norms. Dedicated times for family dinners or social gatherings can create vital moments of joy, showing that mealtime is much more than simply eating; it is a celebration of companionship.
Encouraging communities to embrace this shift not only bolsters personal happiness but might also enhance cultural awareness and appreciation. By making mealtimes events filled with laughter and storytelling, we rekindle the power of social eating, thereby cultivating an environment where happiness thrives. This shift can help diminish isolation and increase overall happiness, prompting a collective reevaluation of how we view our dining practices.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Hunger and Happiness
As we look to the future, addressing the interplay between hunger, social eating, and happiness remains crucial. Researchers are tasked with ensuring that shared meals are effectively integrated into discussions surrounding mental health and societal happiness. Initiatives that connect food security and social gatherings can break down barriers and create pathways to stronger community ties, directly impacting overall happiness.
Moreover, as society evolves, new forms of dining experiences—such as communal kitchens and shared cooking classes—emerge, creating innovative opportunities for social interaction. Assessing the effects of these new formats on both individual well-being and community dynamics could lead to profound insights. Moving forward, there is great potential for shared meals to serve as both a remedy for social isolation and a cornerstone of happiness in our increasingly complex world.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do shared meals contribute to mealtime happiness?
Shared meals significantly enhance mealtime happiness by fostering social connections and creating a sense of belonging. When people dine with others, they often experience greater emotional satisfaction and joy, which are key components of overall well-being.
Is dining with others a reliable indicator of happiness?
Yes, dining with others is a reliable indicator of happiness. Studies indicate that individuals who frequently share meals with friends or family report higher levels of life satisfaction, suggesting that social eating plays a crucial role in enhancing well-being.
What is the relationship between social eating and well-being indicators?
Social eating, or dining with others, serves as an important well-being indicator. Research shows that the frequency of shared meals correlates strongly with positive emotions and life satisfaction, often serving as a more telling metric than income or employment status.
Why are shared meals becoming less common in modern society?
Shared meals are becoming less common due to rising trends of isolation, with many individuals, especially young people, dining alone more frequently. This shift may negatively impact social connections and overall happiness in communities.
Can sharing meals increase individual happiness levels?
While the research currently indicates a strong correlation between sharing meals and happiness, future studies aim to explore whether engaging in more social dining actually increases happiness levels. The idea is that both sharing meals and being happy might influence each other.
What role does community play in dining with others and happiness?
Community plays a vital role in dining with others as it enhances opportunities for shared meals, leading to increased happiness. Greater community engagement can facilitate more social eating experiences, which are instrumental in promoting well-being.
How can policymakers encourage shared meals to improve social well-being?
Policymakers can encourage shared meals by creating initiatives that promote communal dining events, improve public spaces for gatherings, and foster programs that connect individuals, ultimately enhancing social interactions and well-being.
Are there specific demographic trends in social eating related to happiness?
Yes, demographic trends show that social eating habits vary significantly across age groups, with younger populations experiencing a decline in shared meals. Understanding these trends is crucial for addressing social isolation and enhancing community well-being.
What evidence supports the benefits of shared meals on happiness studies?
Happiness studies provide strong evidence supporting the benefits of shared meals, showing that individuals who often dine in groups report higher satisfaction levels. This illustrates the powerful impact of social interactions on emotional health.
How can individuals incorporate more shared meals into their routines?
Individuals can incorporate more shared meals by inviting friends or family over for dinner, joining community groups or clubs focused on cooking, and prioritizing mealtimes as opportunities for social connection, all of which can enhance mealtime happiness.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals and Happiness | Dining with others is strongly correlated with increased life satisfaction and positive emotions. |
| Significance of Findings | Eating together may be as significant an indicator of happiness as income or employment status. |
| Alarming Trends | A growing trend shows more Americans report dining alone, with a 53% increase since 2003. |
| Research Approach | The correlation between shared meals and happiness warrants further research to determine causation. |
| Potential Policy Intervention | Encouraging shared meals could be a strategic starting point for improving societal well-being. |
Summary
Shared Meals and Happiness are intricately connected, as studies show that people who frequently share meals tend to experience greater satisfaction in their lives. The findings highlight the alarming trend of increasing solitary dining among Americans, which could negatively affect overall happiness. Overall, while the evidence suggests that sharing meals is a significant predictor of happiness, future research is needed to fully understand the impact and causal relationships involved. Encouraging communal dining could be a vital step towards addressing social isolation and enhancing well-being within communities.