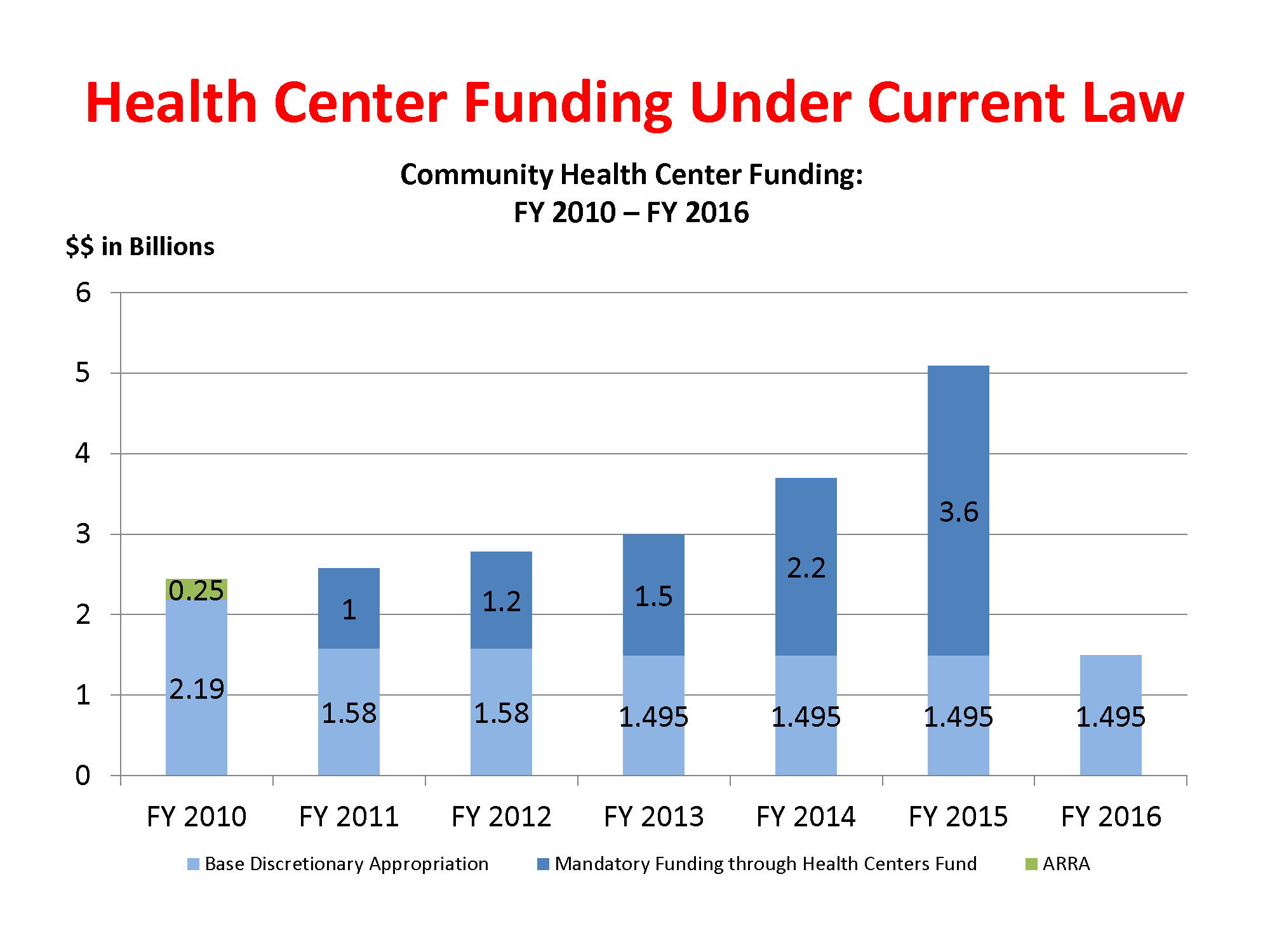
Primary care funding is a critical factor in the ongoing conversation about the future of healthcare in the United States. As demand for accessible medical care increases and the number of available healthcare providers dwindles, primary care faces dire financial challenges. Recent innovations aimed at improving healthcare reimbursement, such as the new ACO PC Flex program, propose a reimagined approach to physician payment models. This initiative seeks to transform funding structures to ensure that primary care providers can deliver preventative care while simultaneously reducing costs associated with hospital visits. By effectively channeling resources into primary care, we can foster medical care innovation that benefits both doctors and patients.
The financial support for primary healthcare services is emerging as a vital topic in discussions pertaining to the overall health system of the nation. Popularly known as primary care financing, this aspect plays a pivotal role in ensuring that healthcare professionals can continue to provide essential services. With the rise of new models like shared savings programs and accountable care organizations, there is a growing focus on improving incentives for general practitioners. These alternatives not only aim to enhance medical care delivery but also prioritize preventative measures, aiming to mitigate future healthcare costs. As the landscape of healthcare reform evolves, understanding funding mechanisms in primary care is more crucial than ever.
Understanding Primary Care Funding Challenges
Primary care funding has long been a topic of concern within the U.S. healthcare system. Despite primary care being the foundation of medical services, it often faces financial constraints that hinder its efficacy. One major oversight in healthcare reimbursement is the disproportionate allocation of funds favoring specialized fields over primary care. This funding disparity often leaves primary care clinicians struggling to meet the growing demand for services, leading to burnout and decreased patient satisfaction.
The Affordable Care Act has introduced numerous provisions aimed at increasing innovative financing models for primary care, yet traditional reimbursement methods still prioritize high-cost specialist visits. These challenges necessitate a shift in physician payment models that recognize the invaluable role of primary care in preventative care and chronic disease management. By addressing these funding challenges, the healthcare system can enhance access to primary care and improve overall health outcomes.
The Importance of Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs)
Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) present a significant shift towards improving the efficiency of primary care delivery through innovative funding models. By incentivizing healthcare providers to focus on quality rather than quantity of care, ACOs encourage collaboration among clinicians to reduce unnecessary hospitalizations and lower healthcare costs. This model aligns physician payment structures with patient outcomes, promoting a healthcare system that prioritizes holistic patient care over mere service volume.
ACOs aim to create a sustainable healthcare environment by rewarding primary care practitioners who successfully manage the health of a patient population. The introduction of ACO PC Flex enhances this model by exploring prospective payment systems that offer upfront funding to primary care practices. This proactive approach allows clinicians to invest in necessary resources and preventative care initiatives, ultimately driving better patient health and reducing reliance on expensive emergency services.
Exploring Innovative Payment Models in Healthcare
As healthcare continues to evolve, innovative payment models are becoming crucial in addressing the systematic flaws in reimbursement structures. Developments such as ACO PC Flex allow healthcare providers to shift from a fee-for-service model to one that compensates for health outcomes and proactive care measures. This transformation is imperative in ensuring that primary care can thrive rather than face continual financial strain.
By implementing payment reform strategies that recognize the importance of preventative care, the healthcare system can not only improve primary care funding but also enhance the quality of care patients receive. Such initiatives pave the way for greater investment in medical care innovation and research, creating a feedback loop where successful primary care leads to healthier populations and reduced long-term healthcare costs.
The Role of Preventative Care in Primary Care Funding
Preventative care plays a pivotal role in the sustainability of primary care funding. It emphasizes the concept that early intervention can help mitigate chronic diseases, ultimately easing the burden on both patients and the healthcare system. Although preventative services have been shown to reduce long-term healthcare costs, current reimbursement structures often fail to adequately compensate primary care providers for these essential services.
To enhance primary care funding, it is crucial to elevate the importance of preventative care within payment models. When primary care providers are incentivized to focus on prevention, they can contribute to a healthier population and lower hospitalization rates. This approach not only reflects a commitment to holistic health but also aligns with the broader goals of medical care innovation in reducing costs and improving patient outcomes.
Redressing Inequities in Primary Care Reimbursement
Significant inequities exist within primary care reimbursement that disproportionately affect lower-income patients reliant on Medicaid. As legislators and healthcare policymakers look to reform the system, it’s vital to address these disparities and ensure equitable access to quality primary care. Current physician payment models often leave Medicaid participants with subpar service options, exacerbating health inequities among populations that require the most assistance.
Improving primary care funding through adjusted reimbursement structures would not only enhance the quality of care received by Medicaid patients but would also provide primary care providers with the necessary financial support to expand services. Addressing this issue can create a ripple effect in improving overall health outcomes and reducing long-term costs associated with untreated medical issues within underserved communities.
Potential Future of Healthcare Reimbursement Models
The future of healthcare reimbursement holds promise for transformative changes, especially with the introduction of models like ACO PC Flex. By establishing a framework that allows for the pre-payment of services, providers can better allocate resources towards preventative care and patient management. This fundamental shift could signal a departure from traditional reimbursement models, paving the way for innovative payment options that prioritize healthier populations.
As these new reimbursement models gain traction, there is hope that they will influence private insurers to adopt similar strategies that reward quality care over volume. If successful, the insights gained from ACO PC Flex and other emerging models could reshape the way healthcare services are delivered, promoting an environment of collaboration among various care providers and ultimately enhancing patient care across all demographics.
Engaging Patients in Their Own Healthcare
A key component of successful primary care innovations lies in engaging patients as active participants in their own healthcare journey. Empowering patients can lead to increased adherence to preventive care protocols and better health outcomes. New payment models integrated with educational resources can help patients understand their health needs and the value of participating in primary care.
By actively involving patients in their care plans, providers can foster a collaborative relationship that encourages lifestyle changes and preventative measures. As a result, care can become more efficient and effective, ultimately reducing healthcare costs and encouraging sustained engagement with primary care services.
The Impact of Corporate Entities on Primary Care
Corporate ownership of primary care practices has raised concerns about the quality of patient care and the financial wellbeing of providers. Often, the focus shifts from patient-centric care to the volume of services delivered, creating a conflict between patient needs and corporate profit motives. Adjustments in primary care funding will require addressing these corporate influences to restore focus to patient health.
The push for accountability and quality in care delivery means that reforms are necessary to mitigate the impact of corporate entities in primary care settings. Advocating for stricter regulations and supportive reimbursement policies can help maintain a healthcare environment where patient care is the priority, ensuring that primary care practices can operate effectively and sustainably.
The Urgency of Addressing Primary Care Scarcity
With a growing patient population and a declining number of primary care physicians, the urgency of addressing primary care scarcity cannot be overstated. As demand for services rises, primary care practitioners find themselves stretched thin, leading to longer wait times and decreased patient satisfaction. Effective strategies for increasing primary care funding are essential to attract and retain talented health professionals.
By improving financial incentives for primary care providers, healthcare systems can encourage more physicians to enter the field, ultimately reducing shortages. This includes redesigning payment models to better compensate the comprehensive roles primary care practitioners play in the healthcare ecosystem, thus ensuring that patients have access to timely and quality medical care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is primary care funding and why is it important?
Primary care funding refers to the financial resources allocated to primary care services, which are essential for maintaining overall community health. This funding supports physicians and healthcare practices in delivering preventative care, managing chronic diseases, and ensuring accessibility to medical services. Adequate primary care funding is crucial as it directly affects the quality of care, reduces healthcare costs by preventing more serious health issues, and helps alleviate the strain on specialized medical services.
How do ACOs impact primary care funding?
Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) significantly impact primary care funding by creating a financial model that incentivizes high-quality care while controlling costs. Under ACOs, healthcare providers receive payments for proactively managing patient health rather than solely for each service provided. This model encourages providers to invest in preventative care and improves the overall efficiency of primary care funding by potentially reducing hospital admissions, thereby saving money within the healthcare system.
What challenges exist in primary care funding?
Challenges in primary care funding include low reimbursement rates for primary care providers compared to specialists, increasing demand for services without a corresponding increase in resources, and systemic biases favoring specialist treatment over primary care. These factors contribute to a shortage of primary care physicians, impacting health outcomes and making efficient healthcare delivery harder to achieve.
What role does preventive care play in primary care funding?
Preventive care is a crucial component of primary care funding, as it helps to identify and manage health issues before they escalate into more serious problems requiring costly interventions. By investing in preventive care, primary care practices can improve community health outcomes and reduce overall healthcare spending. Increased funding for preventive services is essential to empower primary care providers to focus on maintaining health rather than solely treating illness.
What innovations in primary care funding are being introduced?
Innovations in primary care funding include models like the ACO PC Flex, which provides upfront payments to healthcare providers for managing patient health. This prospective payment approach encourages providers to engage more deeply in preventative care and develop infrastructure that supports better health outcomes. Such innovative funding models aim to shift the focus from reactive treatment to proactive management, thereby improving the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
How does healthcare reimbursement affect primary care providers?
Healthcare reimbursement significantly impacts primary care providers by determining their income based on the services they provide. Low reimbursement rates for primary care can discourage physicians from entering or remaining in the field, leading to a scarcity of providers. A fair and adequate healthcare reimbursement model is necessary to ensure that primary care providers are compensated fairly, enabling them to devote the necessary time and resources to their patients.
Could programs like ACO PC Flex replace traditional primary care reimbursement models?
Yes, programs like ACO PC Flex have the potential to replace traditional primary care reimbursement models if they prove successful in improving health outcomes and reducing costs. The shared savings model of ACOs incentivizes better care practices and reduces hospitalizations, making it a compelling alternative to the current fee-for-service system. If this model demonstrates tangible benefits for Medicare recipients, it may stimulate similar approaches in other insurance markets.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| U.S. Primary Care Crisis | Demand for primary care is rising while the number of primary care physicians is decreasing. |
| ACOs and ACO PC Flex | The new program ACO PC Flex aims to increase primary care spending and incentivize preventive care to avoid costly hospital visits. |
| Payment Model Innovations | ACO PC Flex introduces a prospective payment model, giving upfront funding to organizations to facilitate spending on preventive care. |
| Challenges in Primary Care | Low reimbursement rates for primary care compared to specialists and high patient volumes are significant barriers. |
| Potential Impact of ACO PC Flex | If effective, this model could improve primary care funding and patient outcomes, possibly influencing other payment systems if replicated in commercial insurance. |
Summary
Primary care funding is crucial for the sustainability and efficacy of U.S. healthcare. The introduction of ACO PC Flex offers a promising shift in how primary care is financed, emphasizing the need for preventive care and improving the financial stability of primary care practices. By incentivizing a model where physicians can focus on delivering quality care without the pressure of high patient turnover, this initiative could reshape the landscape of primary healthcare, leading to better patient outcomes and more efficient use of resources.