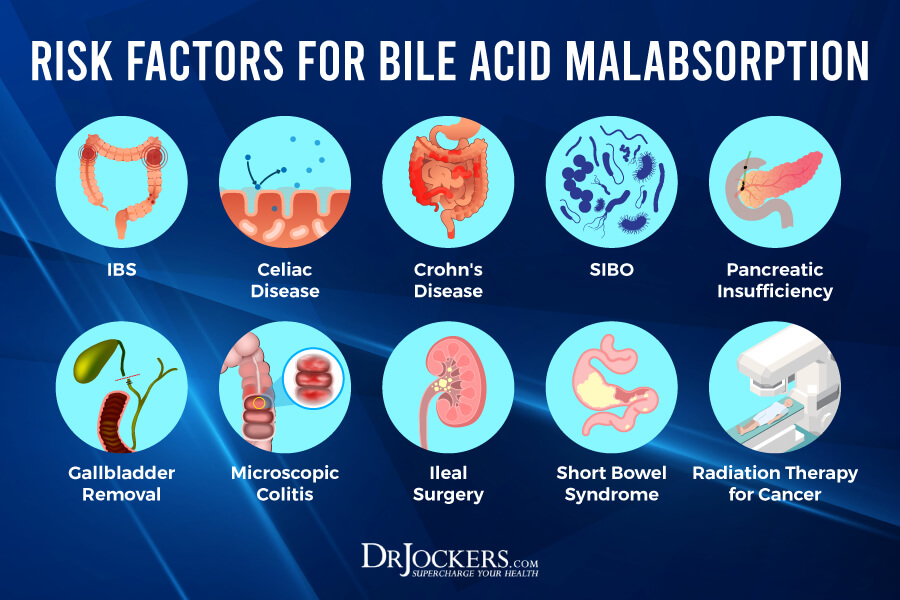
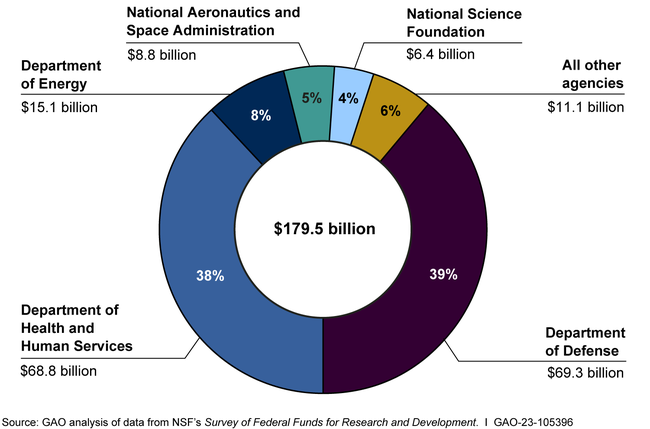
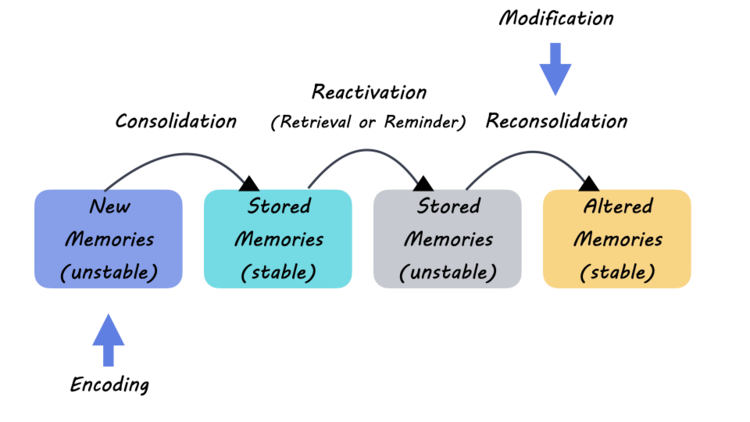
Bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a crucial factor in the development of liver diseases, including liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This imbalance arises when bile acids, the substances produced by the liver to aid fat digestion, are not properly regulated, leading to toxic accumulation in the liver. Recent studies have highlighted the role of key molecular switches in this process, especially the involvement of the YAP protein and the FXR receptor, both of which are essential in maintaining bile acid homeostasis. Disruption of these pathways can result in significant liver injury, inflammation, and a heightened risk of cancer development. Understanding how bile acids influence metabolic processes and cancer progression is pivotal in developing targeted treatments that could revolutionize liver cancer interventions and improve patient outcomes.
The disruption of bile acid regulation, often referred to as bile dysregulation, plays a fundamental role in various liver-related health issues, including malignancies such as hepatic carcinoma. This phenomenon is critical, as bile acids serve dual functions; they not only assist in fat digestion but also regulate metabolic pathways that can influence cellular health. Recent insights have drawn attention to the dysregulation of key players such as YAP, a protein linked to cell growth, and FXR, a nuclear receptor vital for bile acid balance. Their interactions shed light on the underlying mechanisms contributing to liver inflammation and the progression of liver cancer. Exploring alternative terms like bile dysregulation is essential for the comprehensive understanding of how these processes impact health and disease.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Role in Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance refers to the improper regulation of bile acids produced by the liver, which can have serious implications for liver health. Bile acids are essential for the digestion and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins, serving not only as detergents but also playing significant metabolic roles in the body. When bile acids are imbalanced, it can lead to liver injury and subsequent inflammatory processes that heighten the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This liver cancer is particularly concerning as it remains the most common form of liver malignancy, often arising from chronic liver conditions associated with bile acid dysregulation.
Recent research has elucidated the intricate relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer by focusing on the mechanisms that disrupt bile acid homeostasis. Specifically, the activation of the YAP (Yes-associated protein) signaling pathway has been identified as a crucial player in this process. YAP typically promotes cell growth; however, in the context of bile acid regulation, it acts in a detrimental way by inhibiting the action of the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), a key component necessary for maintaining bile acid balance. This disruption leads to an excess accumulation of bile acids, resulting in fibrosis and inflammation that pave the way to liver cancer.
The YAP-FXR Axis: A Pathway to Liver Disease
The interaction between YAP and FXR is central to understanding how bile acid dysregulation contributes to liver cancer. While YAP is known for its role in cell growth and cancer promotion, its function in bile acid metabolism is less recognized. When YAP is activated, it suppresses FXR, which is crucial for sensing and regulating bile acids. This suppression leads to an overproduction of bile acids, cumulatively contributing to liver inflammation and increasing the risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma. This key insight into the YAP-FXR axis reveals potential therapeutic targets to mitigate bile imbalance.
By targeting the regulation of YAP and enhancing FXR function, researchers may be able to devise interventions that prevent the cascade of events leading from bile imbalance to liver cancer. Experimental models have shown promising results with strategies that either activate FXR or inhibit YAP’s repressor activities. These interventions could significantly slow down liver damage and reduce the progression of cancer, highlighting the importance of understanding these molecular pathways in developing new treatments for liver diseases.
Bile Acids: Beyond Digestion to Cancer Progression
Bile acids are not only essential for fat digestion but also play a crucial role in metabolic signaling and maintaining overall liver health. Their hormone-like functions extend beyond simple digestion, influencing pathways associated with inflammation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. A proper balance of bile acids is critical; deviations from this balance can instigate liver injuries that may escalate into more severe conditions, including hepatocellular carcinoma. It showcases the complexity of bile acids as they transition from digestive agents to key players in liver pathology.
Recent studies indicate that the disruption of bile acid homeostasis can lead to a cycle of liver injury and inflammation, eventually leading to cancer. The crosstalk between bile acids and their receptors, such as FXR, illuminates pathways that could be targeted for therapeutic advancement. By manipulating these interactions, especially concerning YAP activation and FXR repression, researchers are uncovering methods to potentially reverse or halt the progression of liver cancer, emphasizing the far-reaching implications of bile acid regulation in liver health.
Therapeutic Implications of Bile Acid Regulation
The discoveries surrounding bile imbalance and its links to liver cancer have significant therapeutic implications. By targeting the key components of signaling pathways such as YAP and FXR, researchers could develop pharmacological interventions designed to restore bile acid homeostasis. Activating FXR function or promoting the excretion of bile acids stand out as promising strategies that could offer new hope for patients at risk of developing HCC due to bile imbalance.
Moreover, the long-term goal of these studies is to translate laboratory findings into clinical applications that can prevent or treat liver cancer more effectively. Targeting the YAP-FXR interaction could lead to innovative treatments that mitigate liver inflammation and fibrosis, potentially transforming how hepatocellular carcinoma is managed. Thus, ongoing research into bile acid metabolism and its regulation will undoubtedly pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies aimed at tackling this prevalent and deadly form of cancer.
Chronic Liver Diseases: The Role of Bile Acids
Chronic liver diseases are often intertwined with bile acid imbalance, which is a critical factor influencing the progression to liver cancer. Conditions like chronic hepatitis, alcohol-related liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are associated with fluctuating levels of bile acids, which exacerbate liver inflammation and damage. Understanding how these conditions impact bile metabolism is vital, as it could unlock new approaches for treatment and prevention, reducing the burden of liver cancer in vulnerable populations.
Moreover, the focus on bile acids has unveiled potential biomarkers for assessing liver disease progression. Research indicates that aberrant bile acid profiles could serve as early indicators of liver dysfunction or cancer risk, leading to prompt intervention strategies. This could be particularly relevant in clinical settings, where having reliable biomarkers can help monitor disease progression and refine treatment options for patients suffering from chronic liver conditions.
Cell Signaling Pathways in Liver Cancer Development
The complexity of cell signaling pathways in liver cancer development emphasizes the importance of research into mechanisms such as those involving YAP and FXR. Signaling pathways not only dictate how cells grow and divide but also how they respond to metabolic cues, including those from bile acids. By delving deeper into these pathways, researchers can uncover additional regulatory nodes that may be exploited for therapeutic gain, enhancing the understanding of liver disease and improving patient outcomes.
Identifying how aberrations in these signaling networks contribute to tumorigenesis highlights potential angles for intervention. For instance, enhancing FXR signaling or counteracting YAP’s negative modulation could help restore cellular balance, thereby reducing the risk of malignancy in the liver. The ongoing exploration of these connections is crucial for developing targeted therapies aimed at correcting the dysregulation that often characterizes liver cancer.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research
The future of liver cancer research appears promising, particularly with the increasing focus on the role of bile acids and their impact on liver function. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of bile acid metabolism and its relationship with signaling pathways like Hippo/YAP, new therapeutic avenues will likely emerge. The interplay between bile acids and liver disease could lead to innovative strategies for preventing and treating hepatocellular carcinoma in the years to come.
Emphasizing a multidisciplinary approach that combines molecular biology, genomics, and clinical research will enhance the understanding of liver cancer etiology. As researchers explore the potential of FXR activation and the modulation of pathways involving YAP, the goal is to develop practical, effective treatments that can significantly improve the prognosis for patients diagnosed with liver cancer. This collaborative effort will be essential in addressing one of the most critical health challenges related to liver diseases.
The Role of Nutrition in Managing Bile Imbalance
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing bile imbalance and supporting liver health. Dietary choices can influence bile acid production and metabolism, thus affecting the risk of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants can help support bile secretion and maintain liver function. Specific foods have been shown to benefit liver health, especially those that promote gut health, as a significant proportion of bile acid metabolism occurs in the gut.
Moreover, certain dietary components may modulate the FXR signaling pathway, thus potentially aiding in restoring bile acid balance. For example, omega-3 fatty acids and polyphenols have been identified as beneficial for liver health. Understanding how nutrition interacts with liver physiology and bile metabolism may lead to dietary interventions that can prevent or mitigate liver cancer risk, paving the way for holistic management strategies.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Liver Health
Making intentional lifestyle changes can significantly support liver health and help manage bile imbalance. Regular physical exercise, for instance, is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, which is crucial given the link between obesity and liver disease. Exercise not only aids in fat metabolism but also enhances liver function, potentially regulating bile acid production in a beneficial manner. Furthermore, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and managing stress can significantly reduce the likelihood of liver inflammation and subsequent injury.
Additionally, adopting practices such as staying hydrated, practicing good nutrition, and ensuring regular medical check-ups can further bolster liver health. These lifestyle strategies can empower individuals to take charge of their health, particularly in the face of risk factors that may lead to bile imbalance and liver cancer. By focusing on comprehensive lifestyle modifications, individuals can enhance their overall well-being while also supporting their liver’s critical functions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is bile imbalance and how is it related to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance refers to the disruption in the production and regulation of bile acids by the liver. This imbalance can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the most common form of liver cancer. A recent study highlights that an overproduction of bile acids, due to the malfunction of the FXR receptor, leads to liver inflammation and ultimately contributes to the development of liver cancer.
How does bile acid metabolism affect liver cancer risk?
Disrupted bile acid metabolism affects liver cancer risk by causing an excess buildup of bile acids in the liver. A key regulator, the YAP protein, interferes with the FXR receptor’s ability to maintain bile acid homeostasis, promoting tumor formation and contributing to liver fibrosis and inflammation, which can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What role does the FXR receptor play in bile imbalance and liver cancer?
The FXR receptor is crucial for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. When bile imbalance occurs, often due to the inhibition of FXR by the YAP protein, it leads to excess bile acid production and accumulation. This can trigger inflammation and ultimately promote the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Can bile acid overproduction cause liver diseases?
Yes, bile acid overproduction can cause liver diseases such as hepatitis, fibrosis, and liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The disruption in the regulatory mechanisms controlled by proteins like YAP and FXR can result in chronic liver injury and inflammation, which increase the risk of developing serious conditions, including liver cancer.
What potential treatments are available targeting bile imbalance in liver cancer patients?
Potential treatments targeting bile imbalance in liver cancer could involve stimulating the FXR receptor or enhancing bile acid excretion methods. Research indicates that activating FXR or reducing the repressive effects of YAP could improve bile acid regulation, decrease liver damage, and potentially halt the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), providing new avenues for liver cancer treatment.
What research advancements have been made regarding YAP and bile acids in liver cancer?
Recent advancements in research have shown that YAP not only plays a role in regulating cell growth but also acts as a repressor of FXR, leading to bile imbalance. This dual function affects bile acid metabolism and promotes liver cancer, suggesting that targeting the YAP-FXR pathway could yield new therapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment.
Is there a link between bile imbalance and liver inflammation?
Yes, there is a strong link between bile imbalance and liver inflammation. The disruption in bile acid regulation leads to an overproduction of bile acids, which accumulates in the liver, causing inflammatory responses. This inflammation can progress to more severe liver conditions, including fibrosis and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A new study found that an imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Mechanism of Action | YAP, a protein, promotes tumor formation by disrupting a bile acid sensor called FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction. |
| Research Findings | The study emphasized the potential for pharmacological interventions by stimulating FXR to mitigate damage from bile acid imbalance. |
| Function of Bile | Bile produced by the liver helps in fat digestion and regulates metabolic processes beyond its detergent function. |
| Future Directions | Enhanced FXR function, inhibiting YAP, and increasing bile acid export are prospect strategies to reduce liver cancer risk. |
Summary
Bile imbalance is a significant health issue that can lead to liver cancer. Recent research has uncovered how disrupted bile acid metabolism, influenced by the YAP protein, can result in hepatocellular carcinoma. By targeting mechanisms like FXR activation, future treatments may help to correct bile imbalances, offering hope in the fight against liver cancer. This underscores the critical link between bile acid regulation and the prevention of serious liver conditions.